It is located in the anterior portion of the abdominal cavity in most vertebrates. As the concentration of sugar in our blood rises the body will try to send insulin to help store this sugar in our bodys cells where it can be used for energy.
Understanding Absorption Rates A S G Sport Solutions
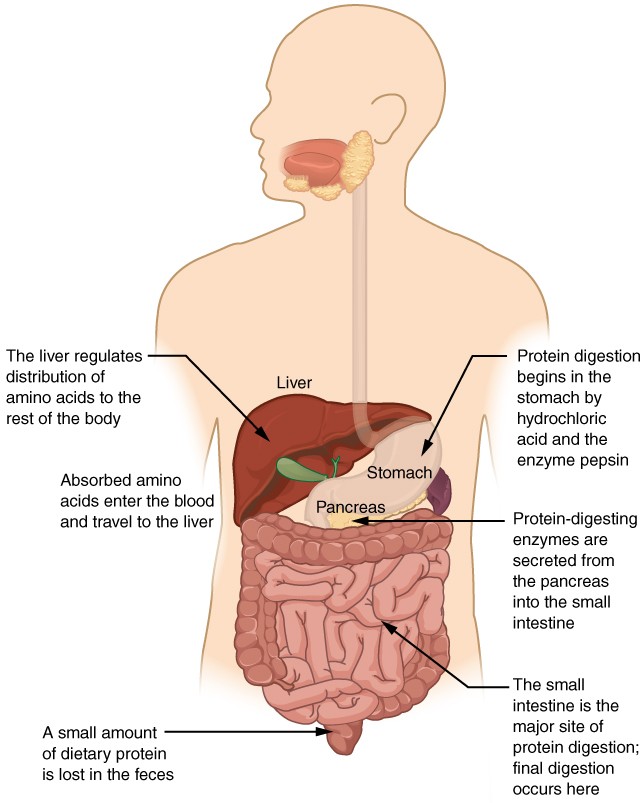
Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Sodium Glucose Cotransporters Functional Properties And Pharmaceutical Potential Sano 2020 Journal Of Diabetes Investigation Wiley Online Library
Cashews contain more total carbohydrate and less fiber than most other nuts.

Where is most glucose absorbed into the blood. But your body also stores some glucose as glycogen most of it in your liver with smaller amounts in your muscles. The stomach serves as a temporary receptacle for the storage and mechanical distribution of food. Insulin restores blood sugar back to normal by transporting glucose into cells that need it for energy or by sending it off to be stored.
Reactive hypoglycemia postprandial hypoglycemia or sugar crash is a term describing recurrent episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia occurring within four hours after a high carbohydrate meal in people with and without diabetes. To be certain of a diagnosis two tests either a fasting glucose or an OGTT should be done at. From there it passes into your bloodstream.
Glucagon is a hormone produced in the pancreas that stimulates your liver to release stored glucose into your bloodstream when your blood sugar levels are too low. This score indicates the increase in blood glucose from a single food containing 50 grams of carbohydrate compared to 50 grams of pure glucose which has a GI score of 100. Your body creates blood sugar by digesting some food into a sugar that circulates in your bloodstream.
When low blood sugar isnt treated and you need someone to help you recover it is considered a severe event. In most cases the after-meal blood glucose rise is barely noticeable. When pasta is cooled down your body digests it differently causing fewer calories to be absorbed and a smaller blood glucose peak.
This is stored in the liver and can be reconverted into glucose when blood-glucose levels fall. The more carbohydrate we eat the more glucose is absorbed into the blood. Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide a subcategory of carbohydratesGlucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide using energy from sunlight where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls the most abundant carbohydrate in the world.
Glucose in the blood stimulates the pancreas to release insulin which then triggers uptake of glucose. As a result the moment blood glucose starts to rise insulin is there to sweep the incoming glucose into the bodys cells. Once in the blood insulin helps glucose get to your cells.
Last format also matters so much liquid carbs will usually increase blood glucose more quickly than solid carbs even if the overall carbs are equal. Its an energy source that fuels your bodykeeping your muscles moving brain thinking and heart pumping. Glucagon a peptide hormone secreted by the pancreas raises blood glucose levelsIts effect is opposite to insulin which lowers blood glucose levels.
Your blood glucose level will spike causing an increased glucose concentration in the pancreas stimulating the release of pre-formed insulin. Glucose Homeostasis and Starvation. But when blood glucose levels are too high most commonly with diabetes it can cause damage to blood vessels and increase the risk of hypertension stroke and heart attacks.
Ethanol mixes with water and it travels readily through cell membranes. Foods that are slowly digested and absorbed - like apples and some bran cereals - trickle glucose into your bloodstream and have low GI scores. An oral glucose tolerance test OGTT GTT may also be used to diagnose diabetes.
The body stores most of its energy as fat. It goes into your intestines where its absorbed. Blood sugar also known as blood glucose comes from the food you eat.
They are absorbed by the digestive tract move into the blood and circulate throughout the body. The term is not necessarily a diagnosis since it requires an evaluation to determine the cause of the hypoglycemia. This glucose will be absorbed into the intestinal epithelium through SGLT receptors apically and then enter your bloodstream through GLUT receptors on the basolateral wall.
In the small intestine glucose is absorbed into the blood and travels to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The hepatocytes liver cells absorb much of the glucose and convert it into glycogen an insoluble polymer of glucose. In addition the more grams of carbs that come from sugar the higher the impact on blood glucose - even if total carbs are the same.
The amylin keeps food from reaching the small intestine too quickly where the nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream. Looking at glucose first when food is consumed there is a corresponding rise and subsequent fall in blood glucose level as glucose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood and then taken up into the cells in the body. The test also tells if you are at the risk of having any kind of complications related to diabetes.
While a blood glucose test tells the levels of your blood glucose on that very day a HbA1c or glycated hemoglobin test informs about how high or low your blood glucose levels have been in the past few weeks or months. Normally blood glucose rises slightly after a meal and the hormone insulin is released by the. Secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose following a meal.
Meal timing especially dinner. Conventional Methods for Glucose Monitoring. It raises blood sugar more quickly than other sugars which.
During digestion the carbohydrates that you eat are broken down into glucose and other nutrients. And reheating it is even better - it reduces the rise in blood glucose levels by a whopping 50 percent. Glucose concentration can be determined using either whole blood plasma or serum samples although the last two are preferred because readings from whole blood are usually 15 lower due to the additional water content in the blood cells As such standard methods require a certain amount of blood meaning they are invasive.
The Role of Glucagon. During times of fasting not eating such as overnight the liver breaks down glycogen and releases it into your bloodstream as glucose to keep your blood sugar levels stable. The balance of insulin and glucagon to maintain blood glucose.
On the other hand fiber slows down the rate at which carbs are digested and absorbed which helps lower blood glucose. Blood glucose or blood sugar is the main sugar found in your blood. The fasting blood glucose level collected after an 8 to 12 hr fast is used to screen for and diagnose diabetes mellitus a fasting sample is used as it is less influenced by time and amount of recent food intake.
Glucose is absorbed directly across the lining of the small intestine into your bloodstream which delivers it to your cells 4 5. Stomach saclike expansion of the digestive system between the esophagus and the small intestine. Your body is designed.
When it reaches the liver glucagon stimulates glycolysis the breakdown of glycogen and the export of glucose into the circulationIn these ways the effects of glucagon are catabolic breaking down cells. Ethanol from alcoholic beverages is absorbed directly through the lining of the digestive tract mostly the stomach and small intestine. It is a small molecule so it doesnt need further breakdown before it can be absorbed.
Insulin lowers blood glucose by increasing glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue and by promoting glycolysis and glycogenesis in liver and muscle.

Sucrose Vs Glucose Vs Fructose What S The Difference

Carbohydrate Absorption Nutritional Doublethink

Changing The Way You Learn Quiz

Sugar Absorption Abdominal Key

5 Things Everyone Needs To Know About Blood Sugar
Changing The Way You Learn Quiz
Paper 2 Digestive System Worksheeet Pdf Digestion Gastrointestinal Tract
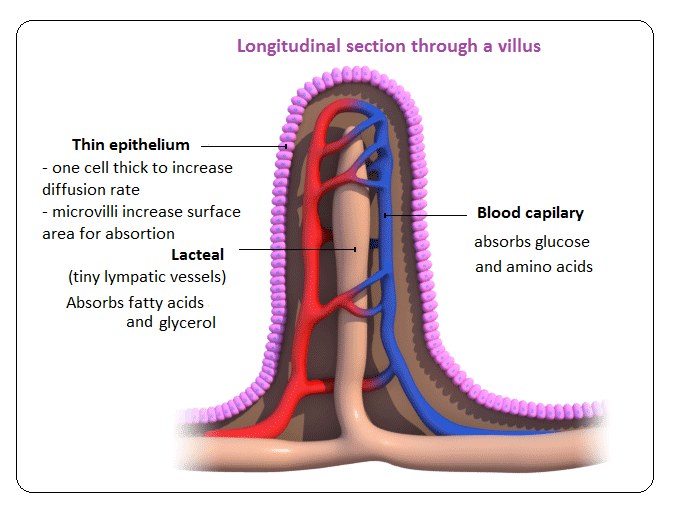
Absorption Function Of The Small Intestine And Significance Of Villi Biology Notes For Igcse 2014

